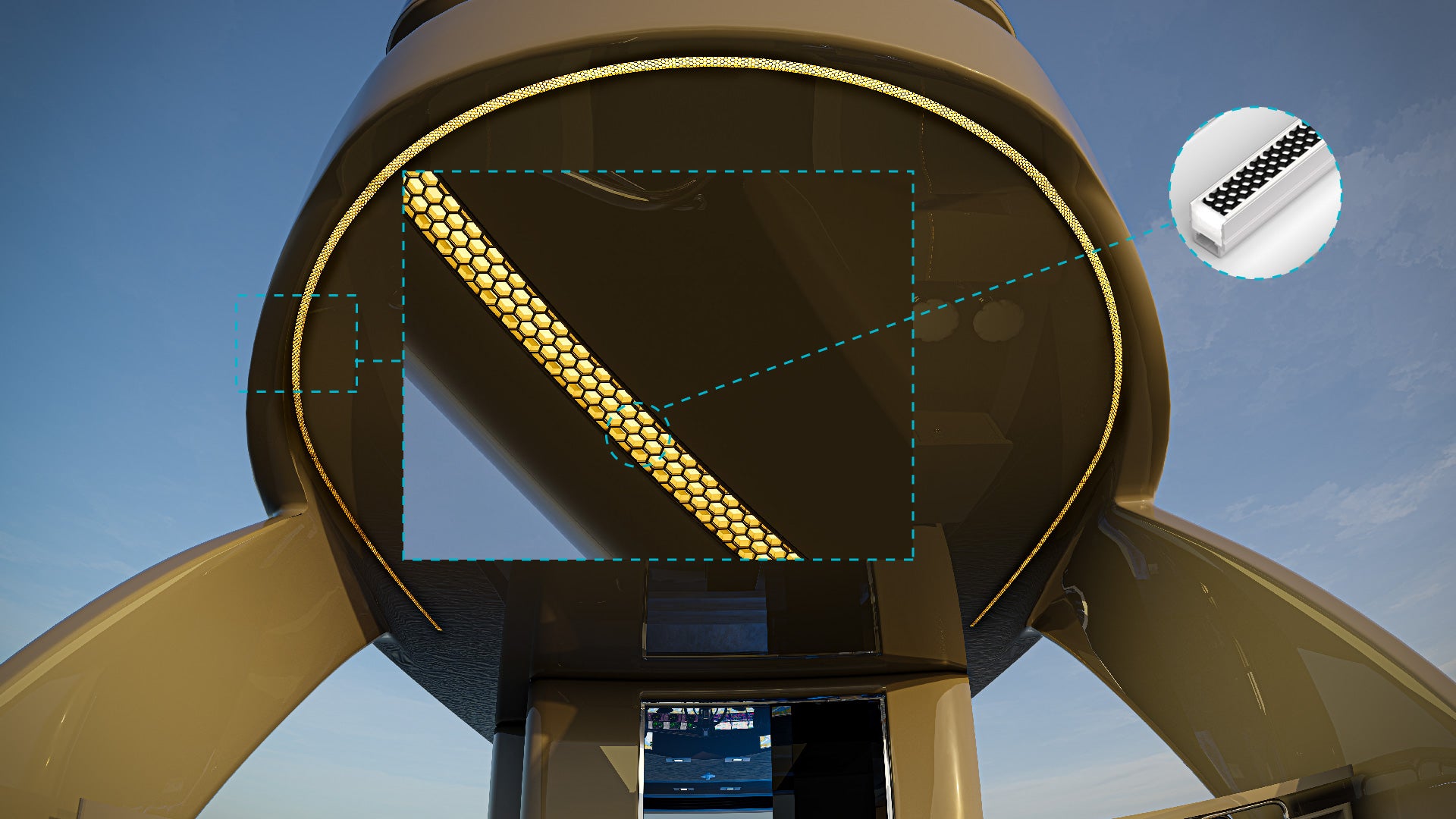
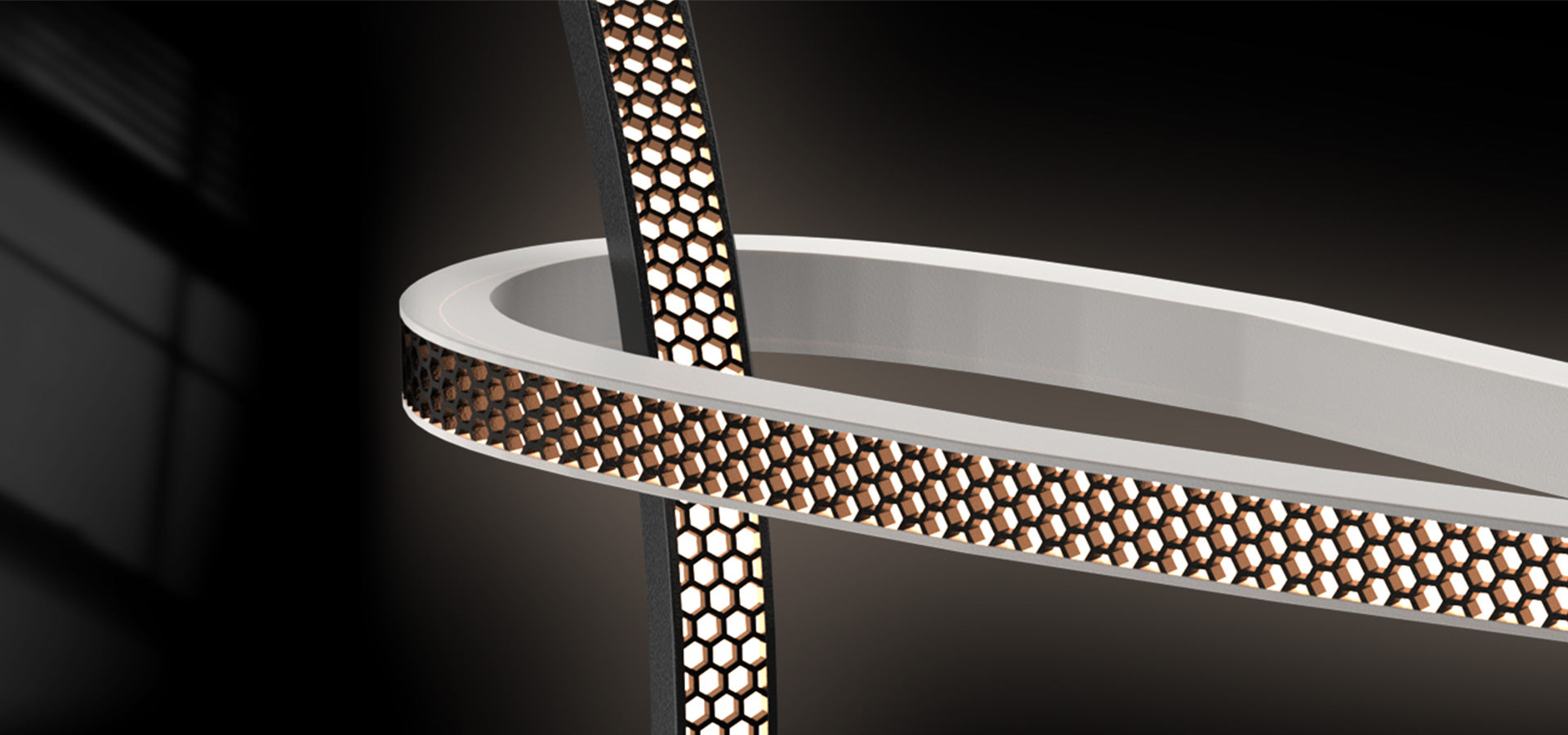
What is Color Temperature?
Color Temperature is a measurement of the color characteristics of light, expressed in degrees Kelvin (K). It defines whether a light source appears more "warm" (yellow/red tones) or "cool" (blue tones) to the human eye. This concept is crucial in lighting design because it significantly affects the mood, functionality, and overall ambiance of a space, whether it’s indoors, outdoors, or in a marine environment.
Warm Color Temperatures (2,000K - 3,000K)
Light sources with lower color temperatures, typically ranging from 2,000K to 3,000K, produce a warm, amber glow similar to candlelight or traditional incandescent bulbs. These warmer tones are often used in spaces where a cozy, relaxed atmosphere is desired, such as living rooms, bedrooms, or yacht cabins. They create an inviting ambiance and are ideal for applications where comfort and relaxation are the main focus.
Cool Color Temperatures (4,500K - 6,500K)
In contrast, light sources with higher color temperatures, generally ranging from 4,500K to 6,500K, emit a cooler, bluish-white light. This type of light mimics daylight and is excellent for areas where clear visibility and alertness are needed, such as kitchens, workspaces, or outdoor decks on boats. Cooler color temperatures are often preferred for task lighting and areas where precision and attention to detail are important because they enhance visibility and reduce eye strain.
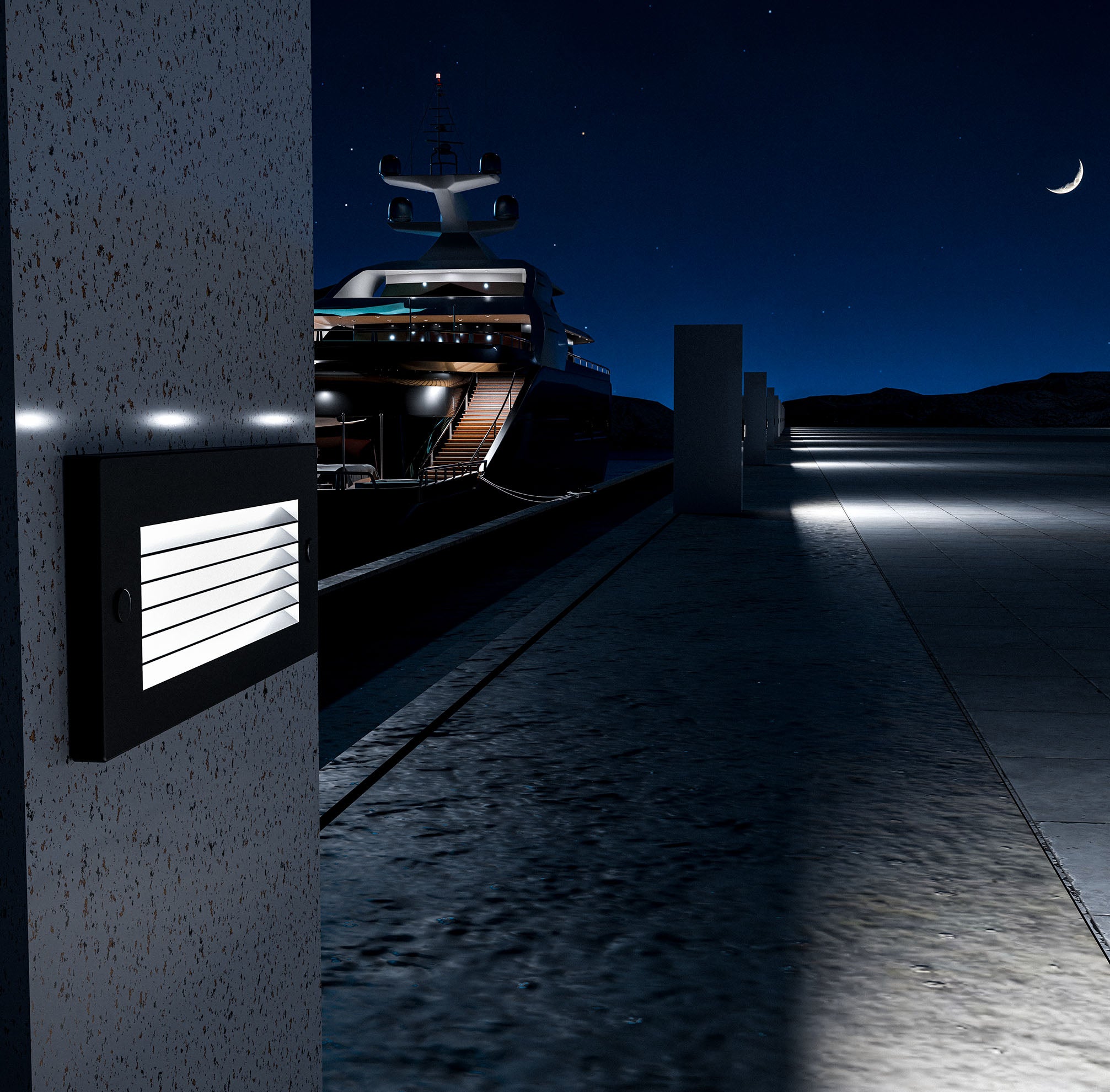
Choosing the Right Color Temperature for Marine Lighting
In marine lighting, selecting the right color temperature is crucial for safety, functionality, and aesthetics. For example, cooler color temperatures are ideal for task-oriented areas on a boat, like the helm or deck, where bright, clear light is essential. Warmer color temperatures, on the other hand, are often used in cabin areas or for accent lighting to create a more relaxing atmosphere. Understanding and choosing the correct color temperature ensures that marine LED lighting systems provide the right balance of illumination, enhancing both safety and comfort for boaters.
For more information on Color Temperature, click here: https://k2lighting.com/blogs/news/marine-led-color-temperature-explained