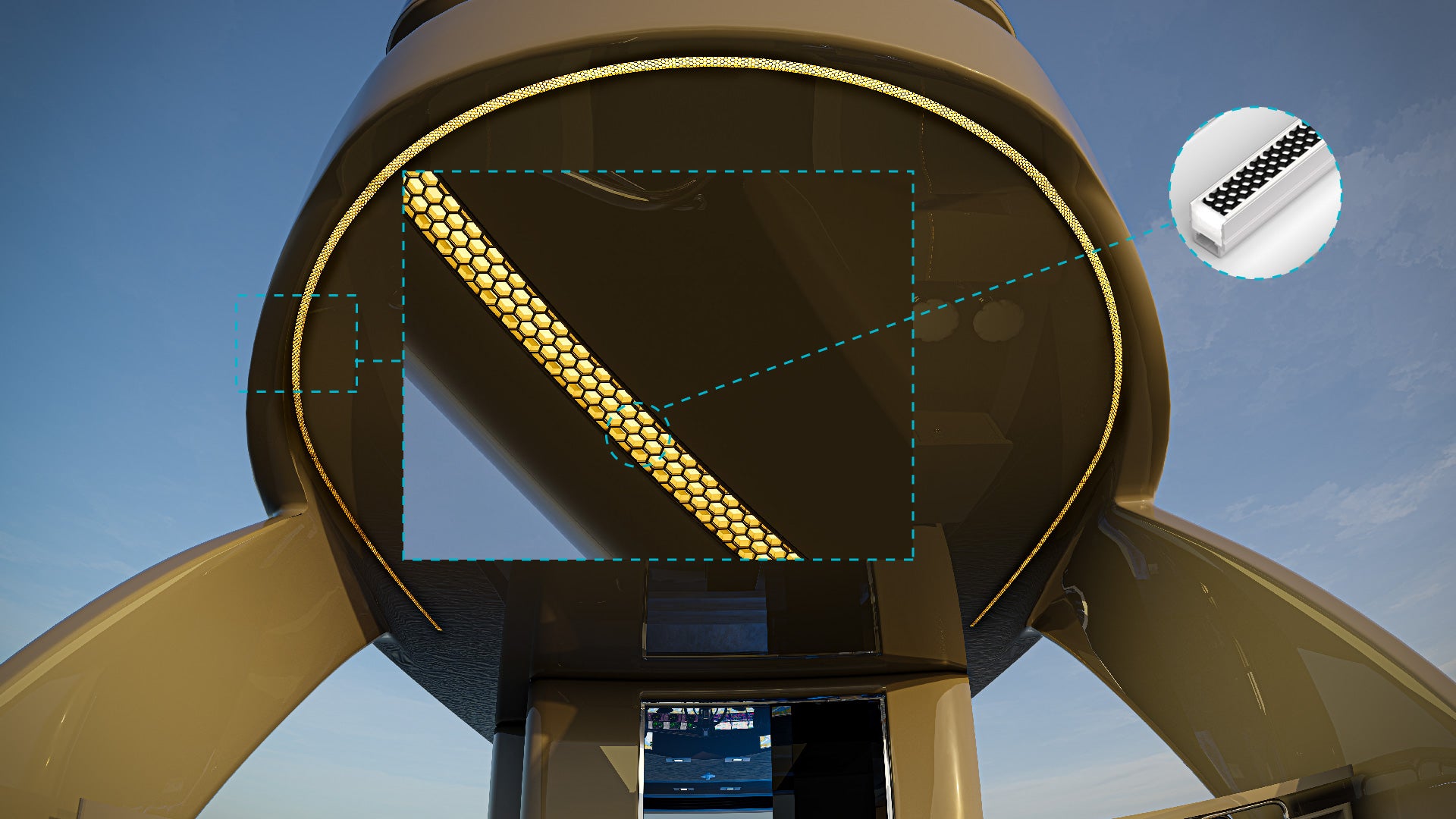
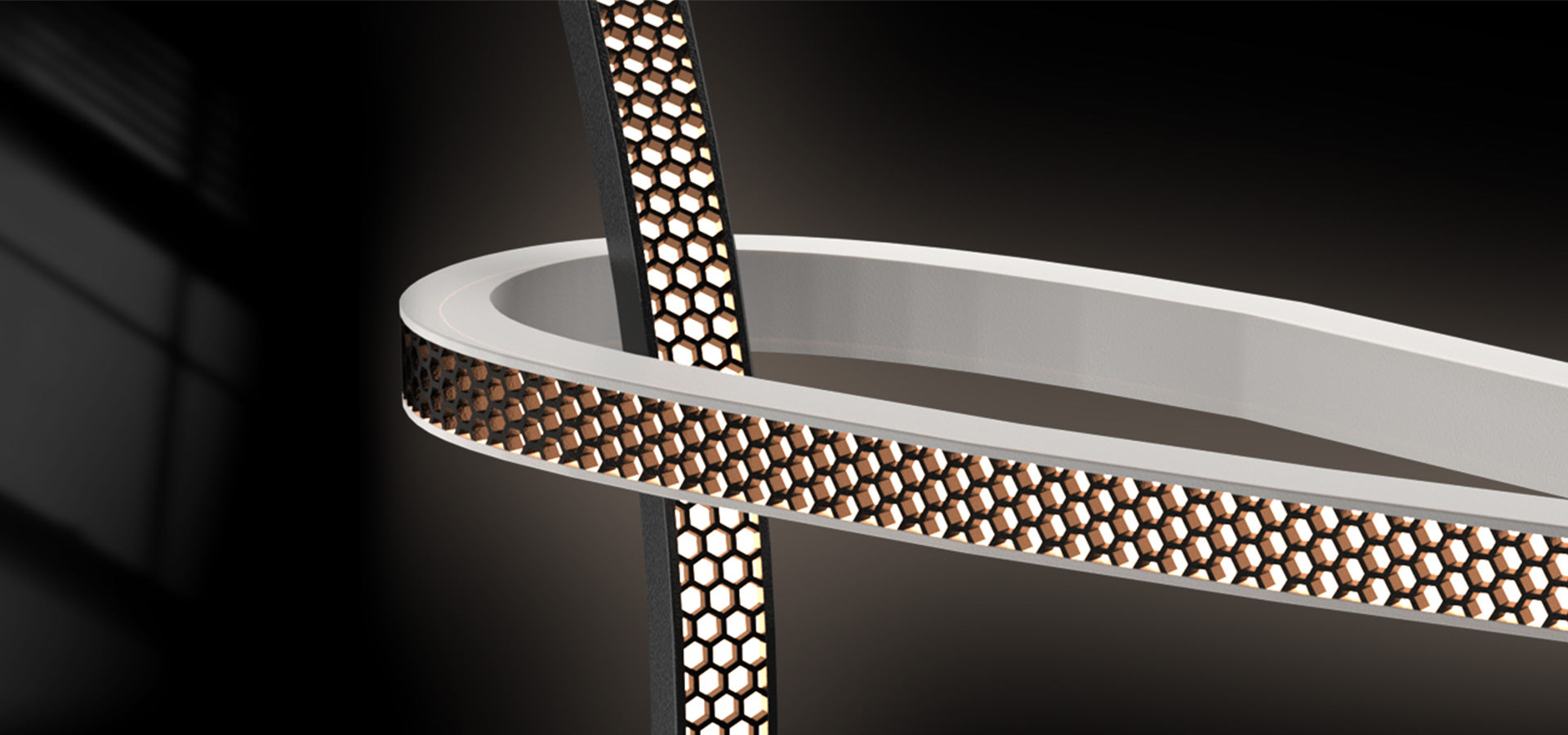
What is Voltage (Volts)?
Voltage is a measure of electrical potential difference, indicating the force that pushes electrical current through a circuit. In the context of boat lighting and electrical systems, voltage is a critical parameter that determines the compatibility and safe operation of devices on board. Voltage, expressed in volts (V), is essential to understand because using the correct voltage helps prevent issues like overheating, inefficiency, or potential damage to equipment. Boats typically operate on 12V, 24V, or 48V systems, depending on the vessel’s size, power needs, and onboard equipment.
Types of Voltage
The type of voltage system a boat uses has significant implications for lighting and other electrical components. Smaller recreational boats commonly use 12V systems, which are ideal for basic lighting, navigation, and other low-power devices. Larger vessels, such as yachts or commercial boats, may use 24V or 48V systems to accommodate higher power requirements for more complex setups, including powerful lighting systems, navigation equipment, and appliances. Understanding the boat's voltage system helps ensure that all equipment is compatible, promoting safer operation and maximizing efficiency.
Voltage Management
Voltage management is particularly important in marine environments due to the finite power resources on most boats. Since the electrical systems on boats often rely on batteries, it’s essential to use fixtures and appliances with the correct voltage to avoid overloading circuits and depleting battery reserves too quickly. Using devices that match the boat’s voltage system can help maintain battery life and optimize power usage, especially on longer trips where energy conservation is key. For example, LED lights designed for 12V systems are highly efficient, providing adequate brightness without taxing the battery, making them ideal for smaller boats and extended journeys.
In addition to matching voltage, many boats employ voltage regulators and converters to stabilize power output and allow for multi-voltage compatibility. Voltage regulators help maintain a consistent voltage, even as batteries discharge, protecting sensitive electronics from fluctuations that could cause malfunctions or damage. Converters are also commonly used to step voltage up or down, enabling the safe use of equipment with different voltage requirements. Understanding voltage, along with the boat’s power setup, allows boaters to safely and effectively manage their onboard electrical systems, ensuring that lighting, navigation, and other critical devices perform optimally throughout their journey.