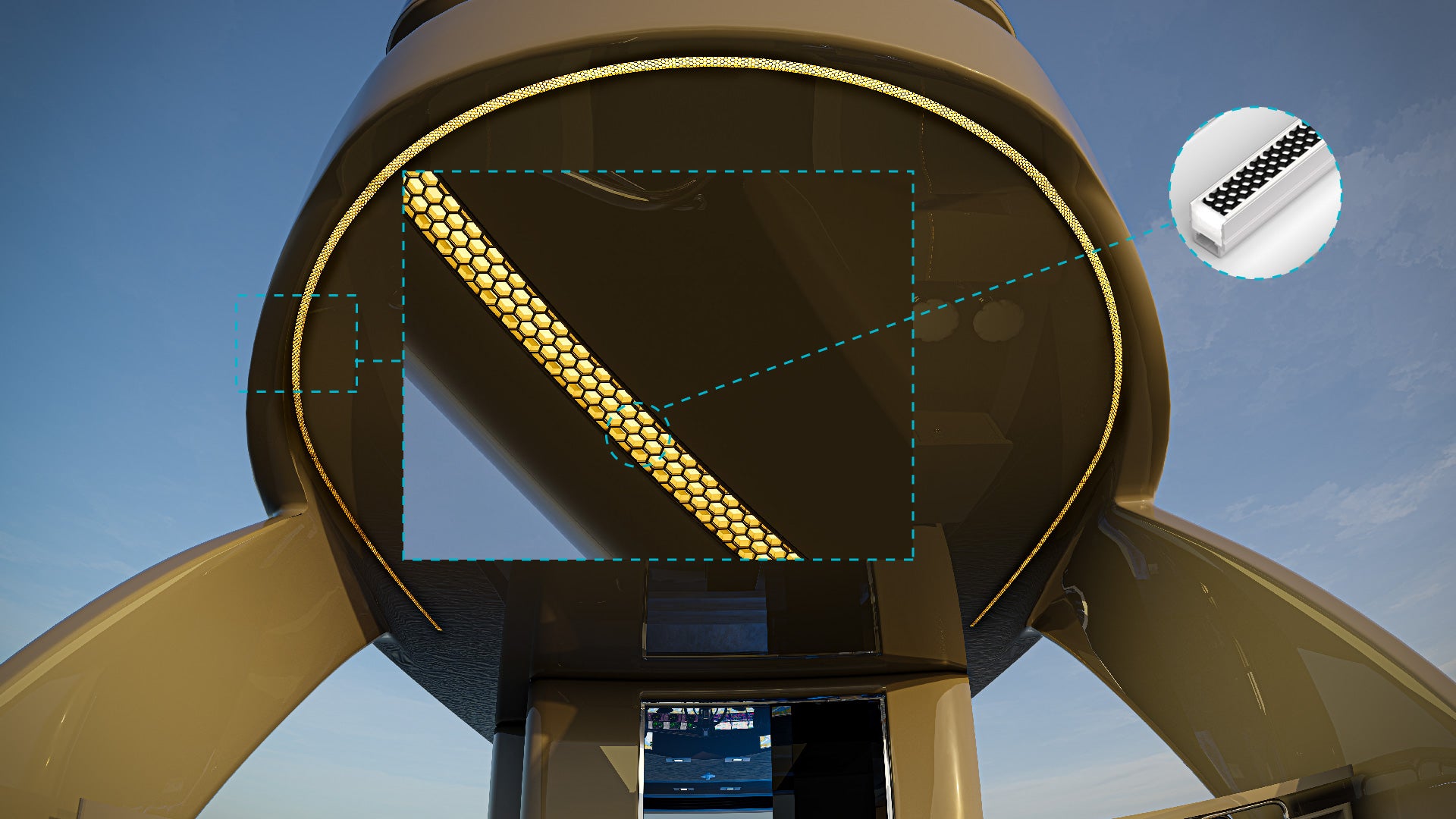
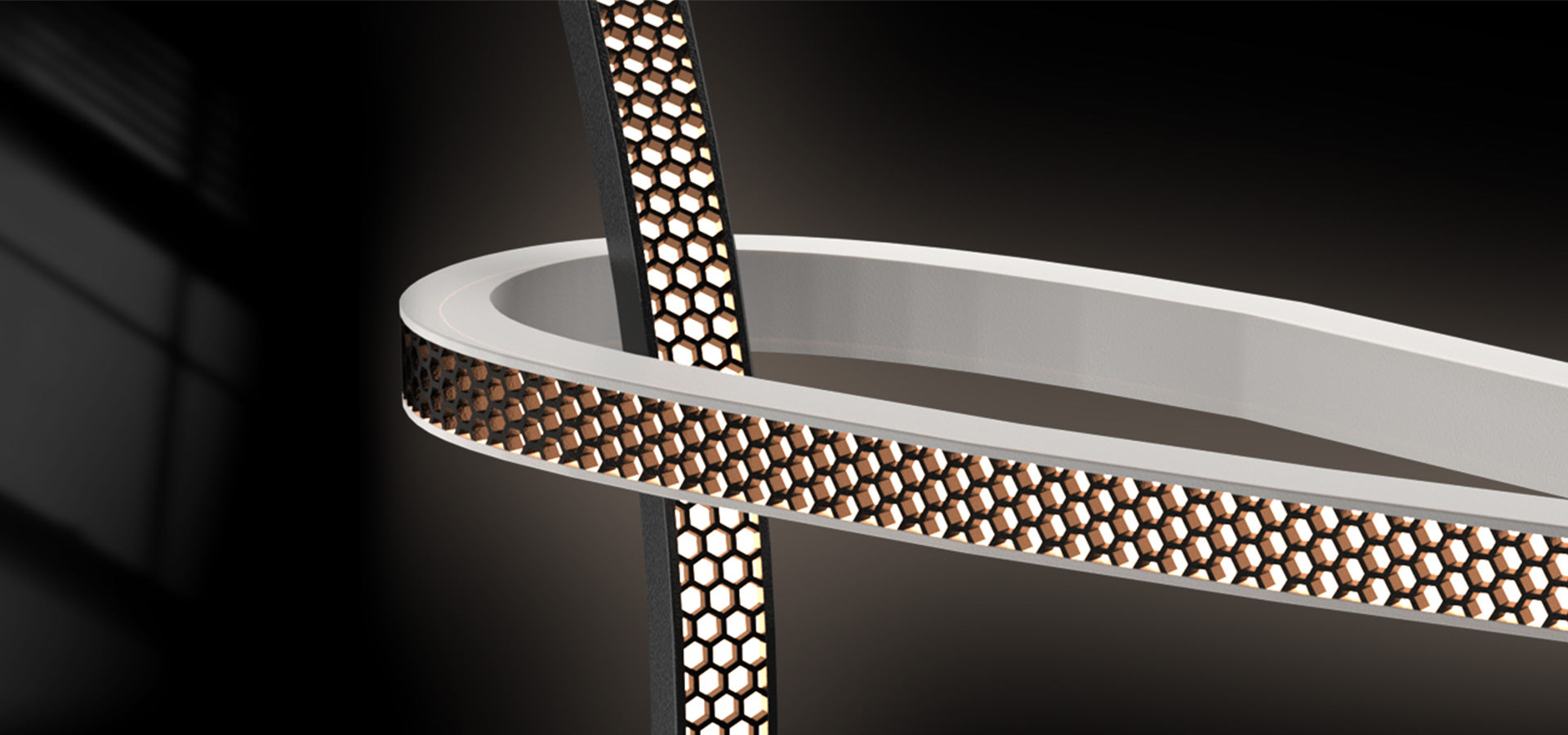
What is Wattage (Watts)?
Wattage is a measurement of power consumption in electrical devices, expressed in watts (W). In the context of boat lighting, wattage indicates how much energy a light fixture uses, but it doesn’t necessarily reflect the brightness of the light produced. Traditionally, higher wattage was associated with brighter lighting in incandescent bulbs, but with advancements in LED technology, wattage and brightness are no longer directly correlated. Instead, wattage in LED lighting helps determine energy efficiency and power usage, making it a crucial consideration for marine lighting where energy conservation is often essential.
Context about Wattage
In marine environments, particularly on boats that rely on batteries or have limited power sources, choosing lighting with appropriate wattage can significantly impact energy efficiency and battery life. Lower-wattage LED fixtures, for example, can produce the same brightness as higher-wattage incandescent bulbs while consuming less energy. This efficiency is especially important for boats operating on extended trips, as it allows for sustained lighting without rapidly draining the vessel’s power reserves. By selecting low-wattage yet high-output LED fixtures, boat owners can ensure they have sufficient lighting while preserving battery power for other critical systems.
How Wattage Generates Heat
Wattage also plays a role in heat generation. Higher wattage typically means more energy is lost as heat, which can be a concern in enclosed spaces on a boat where excess heat buildup can be uncomfortable or even dangerous. LEDs, which operate on lower wattage, produce much less heat than traditional incandescent or halogen bulbs, making them a safer and more practical choice for confined cabin areas or spaces with limited ventilation. This reduced heat output not only improves comfort on board but also lowers the risk of heat-related damage to fixtures and surrounding materials.
How to Select Lights based on Wattage
When selecting lighting for specific areas on a boat, understanding wattage can help boat owners and designers strike a balance between brightness, energy use, and heat production. While wattage indicates power consumption, it should be considered in conjunction with lumens, the measure of light output, to find lighting that is both energy-efficient and sufficiently bright. This balance is essential in marine environments, where power resources are finite and safety is paramount. By carefully choosing low-wattage, high-efficiency lights, boaters can optimize their lighting setup for longer trips, better battery management, and improved onboard safety.