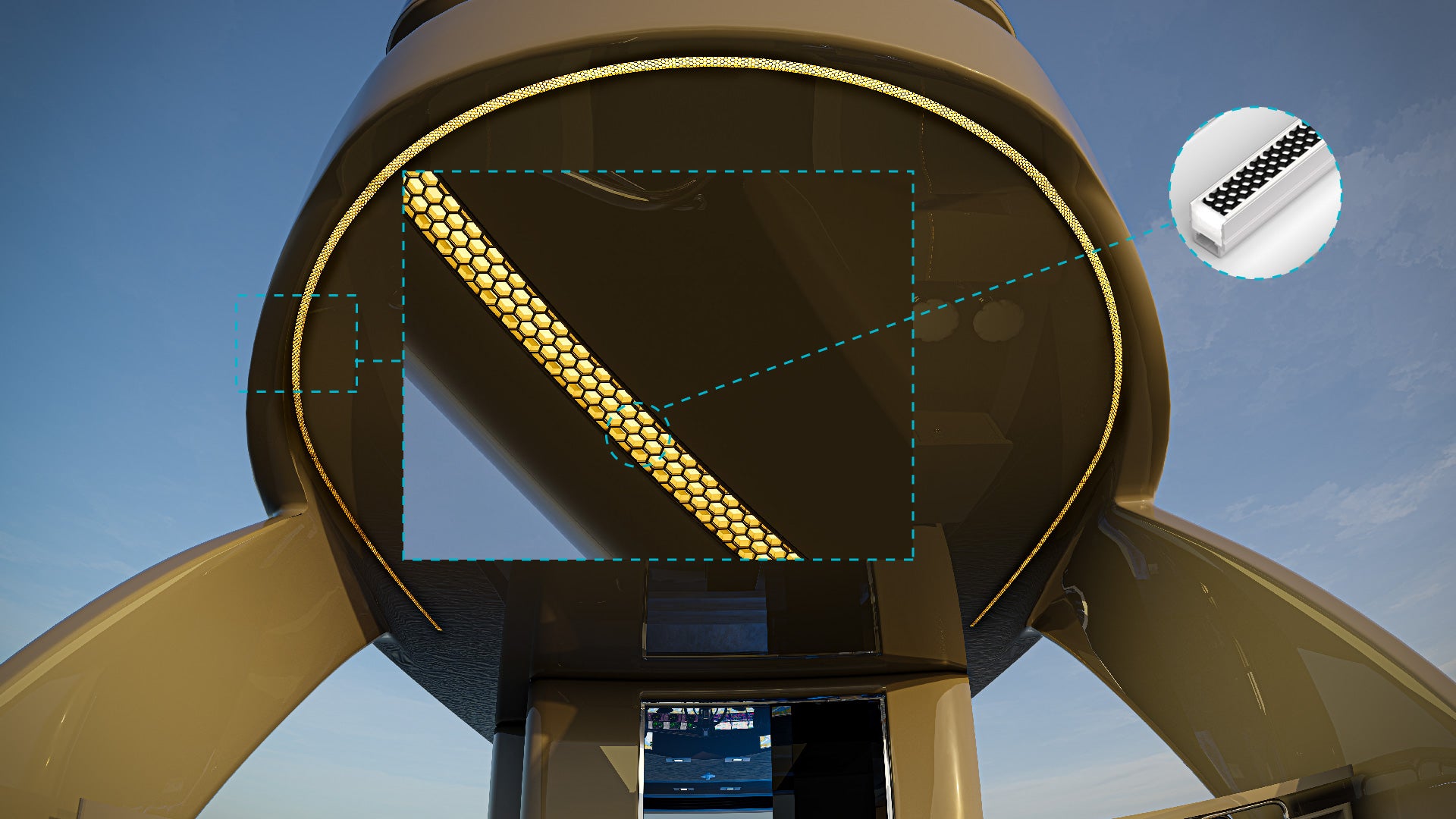
Lighting plays a crucial role in a variety of applications, from enhancing the ambiance of a space to ensuring safety and productivity. The science of photometrics is essential for understanding and optimizing the performance of lighting systems. This comprehensive guide will delve into the fundamentals of photometrics, explaining key measurements and their applications in different lighting scenarios.
What is Photometrics?
Photometrics is the science of measuring visible light in terms of its perceived brightness to the human eye. It involves quantifying light sources, distribution, and intensity to ensure that lighting systems meet specific requirements. In the lighting industry, photometric data is critical for designing effective lighting solutions that maximize both functionality and aesthetic appeal.
Key Photometric Terms and Measurements
Luminous Flux (Lumens)
Definition and Significance: Luminous flux measures the total amount of light emitted by a source in all directions. It is expressed in lumens (lm) and indicates the perceived power of light.
How it is Measured: Luminous flux is measured using integrating spheres and photometers that capture the total light output from a source.
Luminous Intensity (Candelas)
Definition and Applications: Luminous intensity measures the amount of light emitted in a particular direction. It is expressed in candelas (cd) and is crucial for applications where directional lighting is important, such as headlights and spotlights.
Measurement Techniques: Goniophotometers are used to measure luminous intensity by rotating the light source and measuring the emitted light at various angles.
Illuminance (Lux)
Definition and Importance in Different Settings: Illuminance measures the amount of light falling on a surface, expressed in lux (lx). It is critical for determining the adequacy of lighting in various environments, such as workplaces, schools, and public areas.
How to Measure Illuminance: Lux meters are used to measure illuminance by placing the sensor on the surface being evaluated.
Luminance (Nits)
Definition and Visual Impact: Luminance measures the brightness of a surface as perceived by the human eye, expressed in nits (cd/m²). It is important for ensuring that displays and illuminated surfaces are adequately bright and comfortable to view.
Measurement Methods: Luminance is measured using photometers or luminance meters, which assess the light emitted or reflected from a surface.
Tools and Techniques for Measuring Photometrics
Photometers and Lux Meters Types and Functionalities:
These devices are used to measure various photometric quantities. Handheld lux meters are common for measuring illuminance, while more sophisticated photometers can measure multiple parameters.
Spectroradiometers Role in Measuring Light Spectra:
Spectroradiometers measure the spectral power distribution of a light source, providing detailed information about its color characteristics and quality.
Goniophotometers Usage in Measuring Light Distribution Patterns:
These devices measure the angular distribution of light from a source, essential for designing lighting systems that require precise control over light direction and spread.
Applications of Photometric Measurements
Architectural Lighting Enhancing Aesthetics and Functionality:
Photometric data helps design lighting that highlights architectural features while providing adequate illumination for occupants.
Industrial and Commercial Lighting Improving Safety and Productivity:
Proper lighting in industrial settings reduces accidents and enhances worker efficiency. In commercial environments, it improves customer experience and employee productivity.
Outdoor and Street Lighting Ensuring Visibility and Security:
Photometric measurements ensure that outdoor lighting provides sufficient visibility for pedestrians and drivers, enhancing safety and security.
Entertainment and Stage Lighting Creating Desired Effects and Ambiance:
Photometric data is used to design lighting that creates specific moods and effects for theatrical productions, concerts, and other events.
Advances in Photometric Technology
Innovations in Measurement Tools:
New technologies are making photometric measurements more accurate and accessible, including advancements in portable devices and software.
Impact of LED Technology on Photometric Practices:
LEDs offer greater control over light output and distribution, enhancing the precision of photometric measurements and applications.
Future Trends in Photometric Research:
Emerging trends include the integration of smart lighting systems with real-time photometric monitoring and adaptive lighting solutions that respond to environmental changes.
Understanding photometrics is essential for designing effective lighting solutions that enhance safety, functionality, and aesthetics. By leveraging photometric data, lighting professionals can create optimized lighting environments tailored to specific needs. For high-quality lighting solutions backed by thorough photometric analysis, consider K2 Lighting, a trusted provider committed to delivering superior lighting designs. Visit K2 Lighting for more information on our extensive range of products and services. Check out our short form explanation of Photometrics as well!